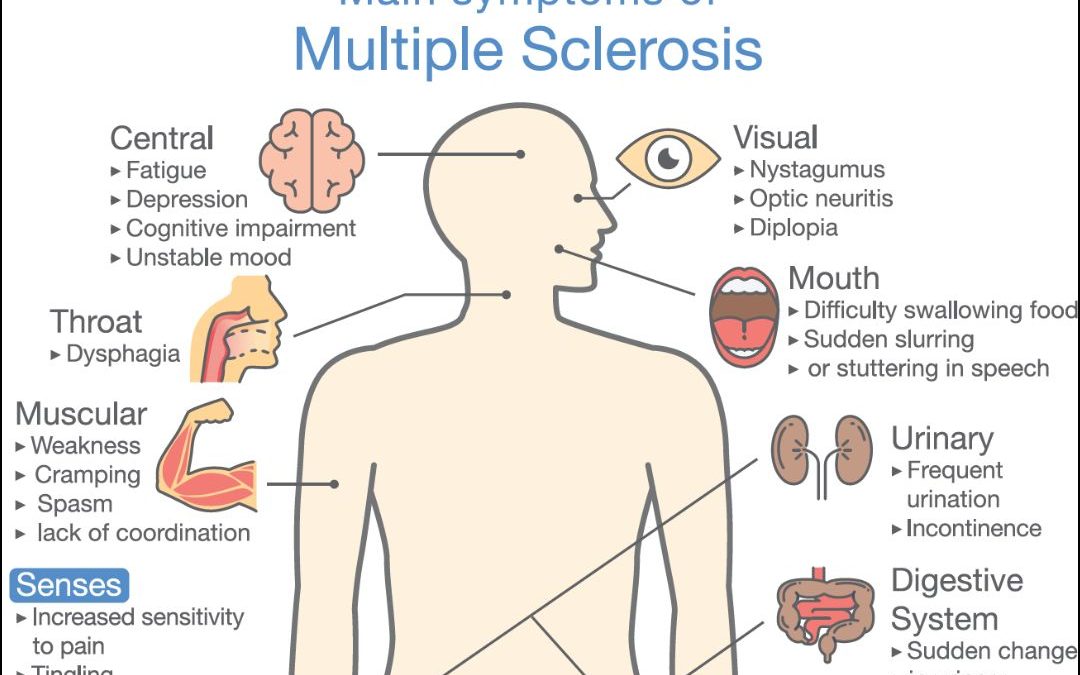
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, leading to a wide array of physical, emotional, and cognitive symptoms. With over 2.3 million people affected worldwide , and no known cure, managing the symptoms of MS is crucial. These symptoms can range from fatigue, chronic pain, and spasticity to cognitive impairments, mobility issues, and depression. Traditional treatments often come with significant side effects, prompting many individuals to seek alternative therapies such as yoga.
Research shows that yoga, a mind-body practice, can offer a safe and effective way to manage MS symptoms. Studies have highlighted its benefits in reducing fatigue, alleviating pain, improving balance and mobility, and enhancing overall quality of life. Mind-body therapies like yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises help individuals with MS manage both the physical and emotional challenges of the disease.
For instance, a study published in Neurology (2016) found that an eight-week yoga intervention significantly reduced fatigue and improved mental health in individuals with MS. Similarly, a systematic review in Multiple Sclerosis Journal (2018) noted improvements in balance, strength, and flexibility following regular yoga practice. Another study in Brain Sciences (2021) emphasized the potential of yoga in improving cognitive function and reducing stress, which are often compromised in MS patients.
Yoga has also been shown to reduce depression, increase strength and flexibility, improve bladder function, and lower stress levels. Specific studies have noted significant improvements in balance, fatigue, and walking speed after consistent yoga practice. For example, a randomized controlled trial published in Disability and Rehabilitation (2014) observed enhanced walking ability and reduced spasticity in participants practicing yoga over 12 weeks.
Therapeutic yoga, which tailors yoga practices to individual needs, offers a holistic approach by addressing not just the physical but also the emotional and mental aspects of MS. Breathing exercises and mindfulness techniques included in yoga help regulate the autonomic nervous system, reducing the impact of stress and promoting resilience.
Despite the promising results, more research is needed to explore the full potential of yoga in MS symptom management. Future studies should focus on diverse populations, various types of yoga, and more rigorously designed trials to fully understand how yoga can best serve those living with MS.
Source: Therapeutic Yoga: Symptom Management for Multiple Sclerosis.
Namaste